Two control methods are supported: PID control and ON/OFF control. Switching between PID control and ON/OFF control is executed by the controller Proportional band parameter.
When parameter Proportional band is set to Zero ,ON/OFF control is selected, otherwise PID control is selected.
PID Control
The output of a PID controller, which is equal to the control input to the plant, is calculated in the time domain from the feedback error. PID controller works in a closed-loop system as follows.
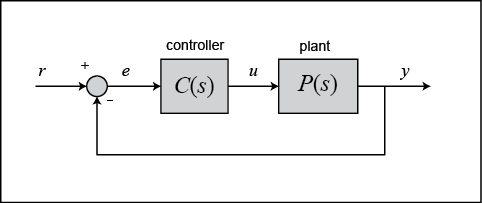
Use autotuning to set the PID constants, or set them manually.For PID control, set the PID constants in the Proportional Band (p), Integral Time (i), and Derivative Time (d) parameters.
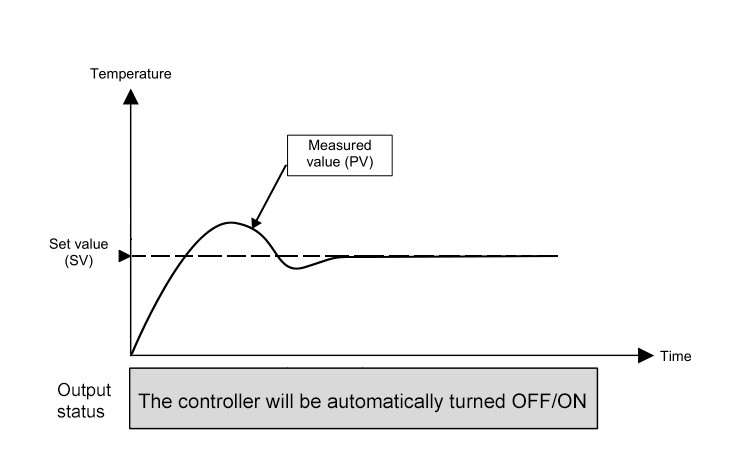
ON/OFF Control
ON/OFF temperature control is the simplest and least expensive form of control available. The output signal from a controller is either FULL ON or FULL OFF depending on the direction of the deviation from a set point.
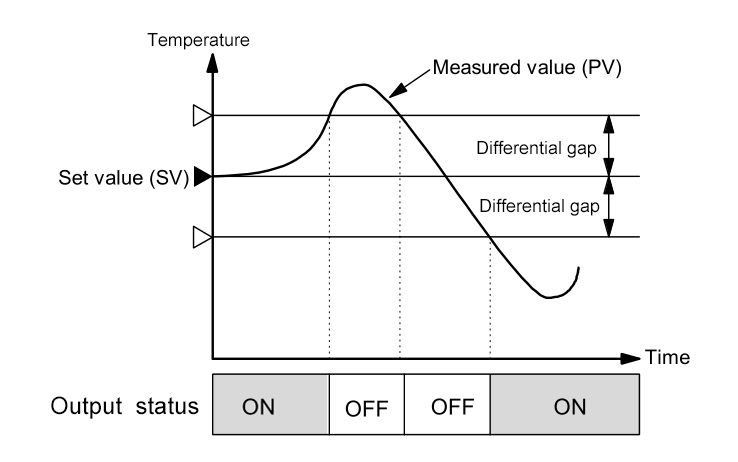
The control output is turned ON when Measured value (PV) less than (Set value (SV)- Differential gap)
The control output is turned OFF when Measured value (PV) greater than (Set value (SV)+ Differential gap)
About PID:
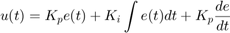
1)Proportional action temperature control is referred to as P or gain. With proportional action, the controlled object no longer switches as a direct result of the set value (SV). The kingcreate instrument compares the difference between the set value and the process variable, then controls the output proportional to the deviation.
This proportional action temperature control is active within user-definable zone around the set point called the proportional band (Pb). When the temperature (PV) enters the proportional band, the output becomes gradually smaller and the temperature stabilizes somewhere within the proportional band.
Proper adjustment of the proportional band will result in smooth control. However, it is seldom that the actual temperature stabilizes exactly on the set point, and it usually becomes stable with some deviation called offset. kingcreate instruments have an adjustable proportional band to meet your process requirements.
2)Integral action temperature control is referred to as I or reset. The degree of integral action is expressed as integral time in seconds. The purpose of the integral action is to automatically compensate for any steady state offset inherent with a proportional controller.
The integral action moves or resets the proportional band up or down depending on the offset. The integral time on kingcreate instruments is adjustable and determines how fast the proportional band is moved.
3)Derivative action temperature control is referred to as D or rate. The degree of derivative action is expressed by derivative time. This action on kingcreate controllers is adjustable in seconds.
The controller measures the rate of the temperature increase and moves the proportional band to minimize overshoot. The output change is directly proportional to the rate of change in the process value (PV).